The nuclear envelope is constructed by the re Biology Diagrams An in vitro nuclear disassembly system reveals a role for the RanGTPase system and microtubule-dependent steps in nuclear envelope breakdown. J. Cell Biol. 178 , 595-610 (2007).

An in vitro nuclear disassembly system reveals a role for the RanGTPase system and microtubule-dependent steps in nuclear envelope breakdown. J. Cell Biol. 178 , 595-610 (2007). The nuclear envelope is punctured by around a thousand nuclear pore complexes, about 100 nm across, with an inner channel about 40 nm wide. [9] Aberrant nuclear envelope breakdown has also been observed in laminopathies and in cancer cells leading to mislocalization of cellular proteins, the formation of micronuclei and genomic instability.

A New Model for Nuclear Envelope Breakdown Biology Diagrams
The COPI complex functions in nuclear envelope breakdown and is recruited by the nucleoporin Nup153. Dev Cell. 2003;5:487-498. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(03)00262-4. This paper implicates the Golgi COPI vesiculation machinery in breakdown of the nuclear envelope. In addition, COPI recruitment to the nuclear envelope is facilitated by its

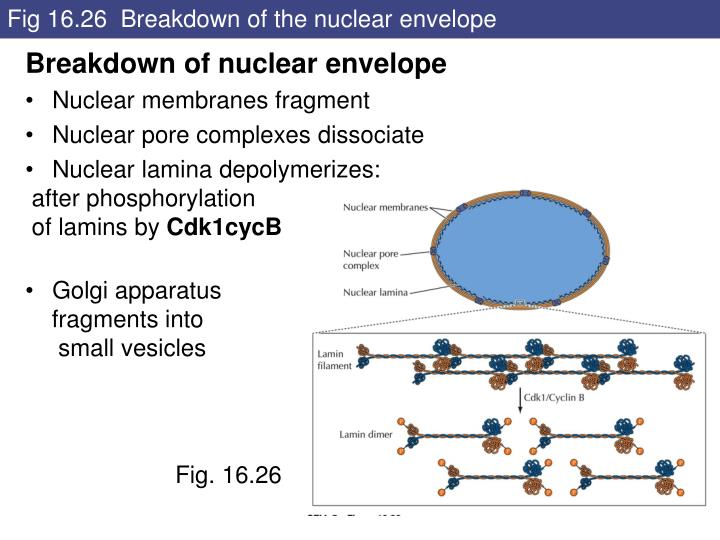
The mechanism of nuclear envelope breakdown (NEBD) was investigated in live cells. Early spindle microtubules caused folds and invaginations in the NE up to one hour prior to NEBD, creating mechanical tension in the nuclear lamina. The first gap in the NE appeared before lamin B depolymerization, at the site of maximal tension, by a tearing mechanism.
Dynamics of Nuclear Envelope Proteins During the Cell Cycle in ... Biology Diagrams
Nuclear envelope breakdown in starfish oocytes proceeds by partial NPC disassembly followed by a rapidly spreading fenestration of nuclear membranes. J Cell Biol 160:1055-1068 [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] Liu J, Prunuske AJ, Fager AM, Ullman KS 2003. The COPI complex functions in nuclear envelope breakdown and is recruited by the

Breakdown and reformation of the nuclear envelope (NE) during cell division is one of the most dramatic structural and functional changes in higher eukaryotic cells. NE breakdown (NEBD) marks a highly regulated switch in chromosome confinement by membranes in interphase to microtubules in M-phase. The boundary of interphase nuclei has a rigid and highly interconnected architecture made up of a
