Centrosome duplication and the cell cycle Biology Diagrams The centrosome duplication cycle occurs in concert with the cell-division cycle. Newly born cells have a pair of centrioles, one engaged orthogonally to the other. Centrioles are generated in new daughter cells through duplication of pre-existing centrioles in the mother cells. Each daughter cell inherits two centrioles (one centrosome) surrounded by pericentriolar material as a result of cell division. However, the two centrioles are of different ages. This is because one centriole originates from the mother cell while the other is replicated from the

In interphase and mitosis, centrosomes play a major role in the spatial organization of the microtubule network. Alterations in centrosome number and structure are associated with genomic instability and occur in many cancers. Centrosome duplication Centrosome duplication is a crucial process ensuring proper cell division, influencing chromosome segregation and overall cellular organization. Errors in this process can lead to aneuploidy or tumorigenesis, highlighting its significance in both normal development and disease. Role In Cell Cycle Progression Centrosome duplication is tightly regulated to ensure each daughter cell inherits

The Centrosome and Its Duplication Cycle Biology Diagrams
However, centrosome duplication and segregation are two equally important events for the two new cells that must inherit a single centrosome. The centrosome, long considered the center of the cell, is made up of two small cylinders, the centrioles, made up of microtubules modified to acquire a very high stability.
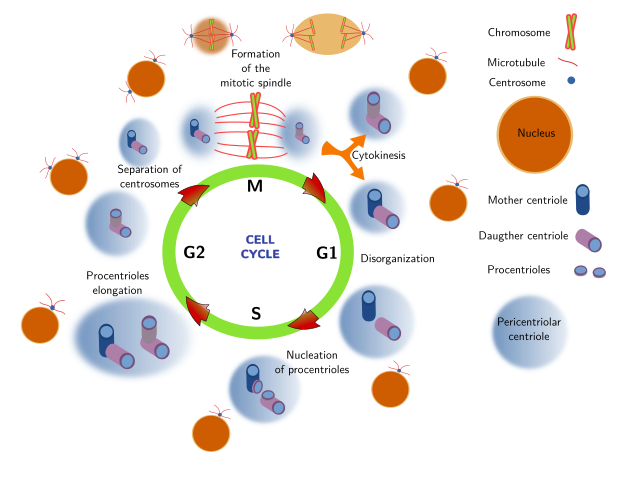
We discuss spatial aspects of the centrosome duplication cycle, the mechanism of centriole assembly and the possible consequences of the inherent asymmetry of centrioles and centrosomes.

The centrosome cycle: Centriole biogenesis, duplication and inherent ... Biology Diagrams
Centrosomes are microtubule-organizing centres of animal cells. They influence the morphology of the microtubule cytoskeleton, function as the base for the primary cilium and serve as a nexus for important signalling pathways. At the core of a typical centrosome are two cylindrical microtubule-based …
